VDE vs XLE - Which Energy ETF Is Better?
Both VDE and XLE focus on providing investors exposure to the energy sector, specifically targeting companies involved in producing and distributing oil, gas, and other energy sources.
These funds could be the key to unlocking the potential of the energy industry, but which one comes out on top?
Let's dive in!
VDE - Vanguard Energy ETF
Goal: The goal of VDE is to track the performance of the US Energy 25/50 Index, providing investors with exposure to companies within the energy sector.
Number of Stocks held: 112
Dividend Yield: 3.41%
Annual Expense Fee: 0.10%
Benefits of VDE: VDE offers investors a low-cost option to gain exposure to the energy sector with a diversified portfolio of 112 energy stocks. This diversification helps reduce the impact of any single company on the overall performance of the fund. Additionally, VDE has a low expense ratio, making it a cost-effective choice for investors.
Downsides of VDE: The energy sector can be volatile, which may lead to fluctuations in the value of VDE. This may not be suitable for risk-averse investors or those with a shorter investment horizon.
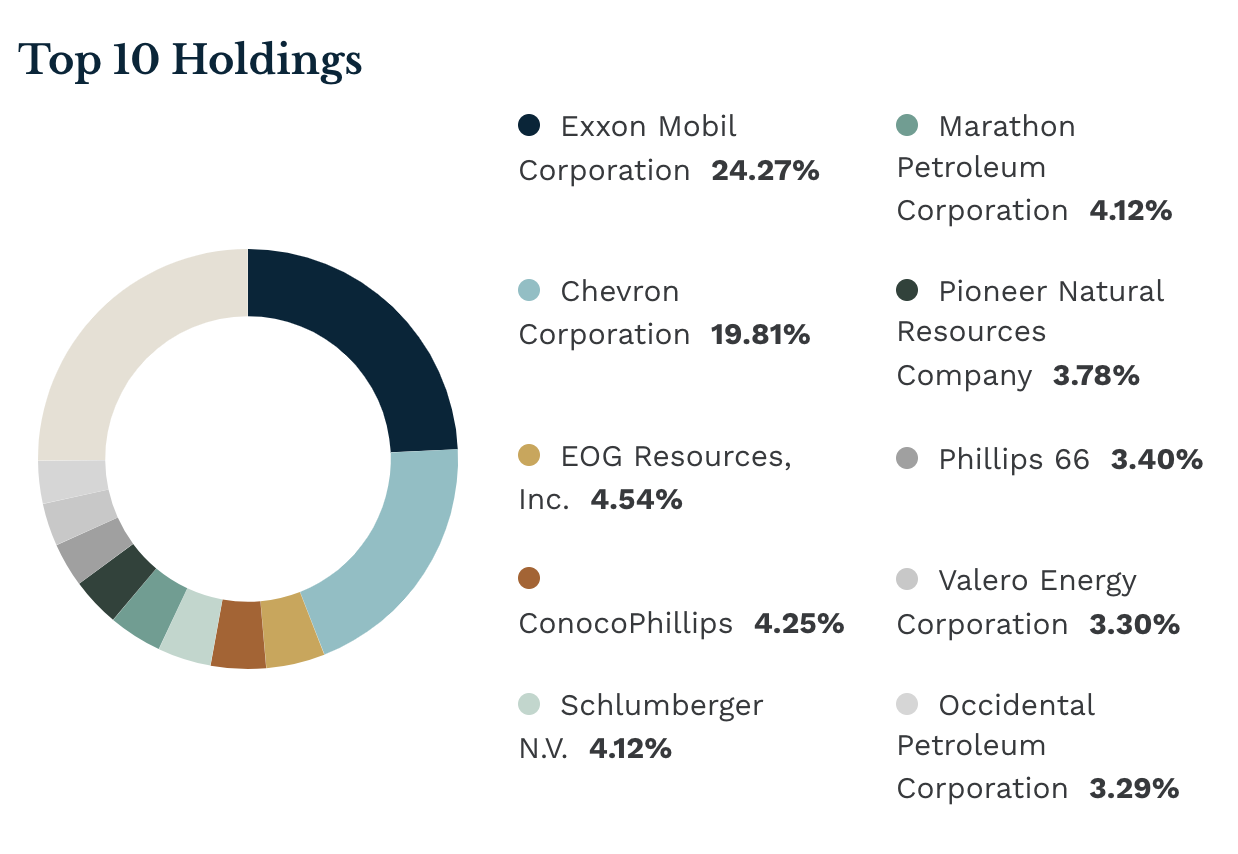
The Top 10 Stocks Held In $VDE:
XLE - Energy Select Sector SPDR Fund
Goal: XLE seeks to track the performance of the Energy Select Sector Index, providing investors with exposure to companies within the energy sector.
Number of Stocks held: XLE holds 23 stocks within the fund.
Dividend Yield: 3.74%
Annual Expense Fee: 0.10%
Benefits of XLE: XLE offers a slightly higher dividend yield compared to VDE, which may be appealing to income-focused investors. The fund is also focused on larger, more established energy companies, which may provide some stability in an otherwise volatile sector.
Downsides of XLE: With only 23 stocks in its portfolio, XLE is less diversified compared to VDE. This may result in a higher concentration of risk for investors, as the fund's performance is more reliant on the success of a smaller number of companies.
The Top 10 Stocks Held In $XLE:
Final Thoughts: VDE vs XLE
VDE and XLE both offer investors a way to gain exposure to the energy sector, but they cater to different preferences.
VDE provides a more diversified portfolio with a lower expense ratio, making it suitable for cost-conscious investors who want broader exposure to the energy sector.
On the other hand, XLE offers a higher dividend yield and focuses on larger, more established companies, making it a potential choice for income-seeking investors who prefer stability.
When looking at the 10-year annual performance, VDE has a return of 3.73% per year, while XLE boasts a higher return of 4.71% per year.
This performance difference may be an important consideration for investors who prioritize long-term growth. However, it is crucial to remember that past performance is not a guarantee of future results.
In summary, these funds could be a great addition to your portfolio if you're looking to invest in the energy sector.
The key is understanding your personal investment goals, risk tolerance, and desired performance to decide which fund best aligns with your strategy.
By the way: Sign up for my email list to be the first to know when I publish a new blog post!
I recently put together a master list of 88 different ETFs designed to support different investment goals. You can grab it here.
And as always: Buy things that pay you to own them.
-Josh
Blog Post: #104